Data tokenization is a method used to protect sensitive information by replacing it with non-sensitive equivalents, or “tokens.” These tokens retain certain essential elements of the original data but have no intrinsic meaning or value on their own. This technique is particularly valuable in environments where secure data transmission, storage, and processing are crucial, such as in finance, healthcare, and emerging Web3 applications.
What Is a Token?
Tokens are digital representations of value or information that reside on a blockchain. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are native coins of their respective blockchains, tokens are built on top of these blockchains using specific standards. Common examples include:
- ERC-20: For fungible tokens on Ethereum
- ERC-721 and ERC-1155: For NFTs and semi-fungible tokens
- BEP-20: For fungible tokens on BNB Chain
Tokens can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Acting as currencies
- Representing ownership of assets (digital or physical)
- Encoding and transmitting data
- Enabling access to services or applications
One growing use case is the tokenization of real-world assets (RWAs) such as real estate, stocks, or gold, allowing these assets to be traded and managed on blockchain platforms.
What Is Data Tokenization?
Data tokenization involves substituting sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers, health records, personal identifiers) with a token that has no exploitable value. The original data is securely stored in a “token vault,” while the token can be used within systems for authorized operations.
For instance, a 16-digit credit card number might be replaced with a randomly generated alphanumeric string. This token can then be used for internal processing without exposing the real card number to risk.
Beyond traditional finance, data tokenization is increasingly being adopted in Web3 ecosystems, enabling users to tokenize their digital identities, social media accounts, and personal data, giving them ownership and control over their digital footprint.
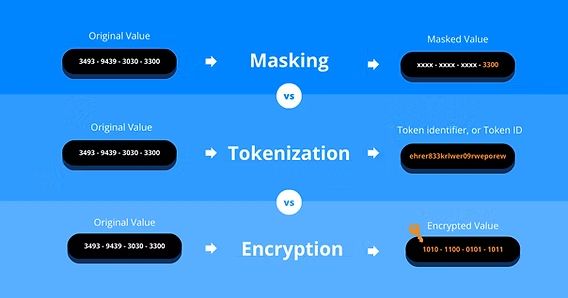
Tokenization vs. Encryption: What’s the Difference?
Encryption and tokenization are both data protection techniques but operate differently:
- Encryption transforms data into unreadable ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms and keys. It is reversible using a decryption key.
- Use cases: secure messaging, encrypted storage, HTTPS protocols
- Tokenization replaces data with tokens without any mathematical link to the original data. It is irreversible unless accessed through the secure vault.
- Use cases: credit card processing, identity management, healthcare compliance
Encryption protects data confidentiality during transit and storage, while tokenization ensures that sensitive data is never exposed in the first place.
How Data Tokenization Works
Here is an example of how tokenization can enhance user control in social media:
- A user has a digital identity linked to a blockchain wallet (e.g., MetaMask).
- The user joins a new decentralized social media platform.
- By connecting the wallet, the user’s on-chain data (e.g., posts, NFTs, contacts) is automatically transferred.
- The user doesn’t need to recreate their profile or content manually.
This enables platform portability, data ownership, and interoperability, allowing users to freely move between services while maintaining control over their digital identity and content.
Benefits of Data Tokenization
1. Enhanced Security
By substituting sensitive data with meaningless tokens, the surface area for data breaches is drastically reduced. Even if a breach occurs, the stolen tokens are useless without access to the vault.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Tokenization helps organizations meet strict regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Since tokenized data is considered non-sensitive, it simplifies compliance procedures.
3. Data Minimization
Tokenization reduces the need to store and handle sensitive data across systems, lowering operational risk and complexity.
4. Secure Data Sharing
Tokens can be shared across departments, platforms, or with third-party vendors without exposing the underlying sensitive data, enabling safe collaboration and innovation.
5. Data Portability and Sovereignty
In Web3 environments, tokenized identities allow users to carry their personal data and content across platforms, reclaiming control from centralized service providers.
Limitations and Challenges
1. Data Quality and Usability
Some systems rely on raw data for functionality. Tokenization can limit capabilities such as real-time personalization or geographic content delivery.
2. Interoperability
Tokens generated in one environment may not be readable or usable in another unless standardized protocols are in place.
3. Governance and Ethics
Who controls the token vault? How is user consent managed? These questions raise legal and ethical concerns around data ownership and privacy.
4. System Complexity and Recovery
A failure in the tokenization system can create data access problems. Restoration requires both the tokenized and original datasets to be managed and recovered accurately.
Real-World Use Case: Social Media and NFTs
Traditional social media platforms collect and monetize user data, often without clear consent. With tokenization, users can:
- Monetize their own data by selectively sharing it with advertisers or researchers
- Create custom access rules (e.g., only verified wallets can view posts)
- Protect their identity and content using smart contracts
This creates new revenue streams for users while promoting privacy and consent-based data sharing.
Future of Data Tokenization
Data tokenization is gaining traction across sectors:
- Finance: Credit card and transaction security
- Healthcare: Secure storage of patient data
- Media: Ownership of digital content
- Government: Digital IDs and records management
As blockchain and decentralized technologies evolve, tokenization will become a foundational layer of the Web3 economy, enabling secure, compliant, and user-controlled data ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Data tokenization is more than a security technique—it’s a paradigm shift in how data is managed and shared. As the demand for privacy, security, and control grows, tokenization will play a key role in shaping the future of digital interactions.
To succeed, organizations and developers must approach tokenization thoughtfully, balancing technological implementation with legal and ethical responsibility. When done right, it empowers individuals and strengthens trust in digital ecosystems.
Join MEXC and Get up to $10,000 Bonus!
Sign Up


