
Preview
This article embarks on the series delving into Yooldo, a blockchain multiverse gaming platform. The series introduces Yooldo’s distinctive projects and applications aimed at contributing to the mass adoption of blockchain technology. In an industry marked by constant challenges and rapid evolution, the Yooldo ecosystem presents a new vision. The platform strategically employs a new profitable and sustainable tokenomics model and a variety of interconnected Play-to-Earn (P2E) based projects. Amidst the emerging industry trends centered around the metaverse, initiatives like Yooldo signify substantial strides toward the Next Big Thing.
In this Yooldo series, we will comprehensively analyze various game projects hosted on the Yooldo platform, aiming to offer meaningful insights into specific challenges encountered by blockchain-based game projects and the essential conditions for the success of the industry. Recognizing GameFi as a key catalyst for blockchain mass adoption, readers can gain a nuanced understanding of the current and future landscape of Web 3.0, as well as the shifting societal discourse on the next-generation internet.
Ultimately, this article seeks to examine the critical challenges faced by the Web 3.0 blockchain-based gaming market as it accelerates towards long-term sustainability. By analyzing the Yooldo platform’s unique vision and groundbreaking implementations, we aim to explore the potential for Blockchain mass adoption in 2024, which is rapidly approaching.
1.0 The Next Web 3.0 Paradigm Renewed Reconstruction of Contemporary Web 3.0 Discourse

Do you remember Web 2.0? Those who have lived through the eras of Web 1.0, 2.0, and the current Web 3.0, alongside the rapid proliferation of hardware, are once again contemplating the era of Web 3.0. The current fervor surrounding the metaverse, blockchain, AI, and Web 3.0 mirrors the significant attention received by the emergence of Web 2.0 in 2006.
Web 2.0 signifies an internet environment where users, through centralized platforms like YouTube and Instagram, become consumers and information producers. The active participation of users in creating and advancing new digital value through platforms is a prominent characteristic of the Web 2.0 era.
The rise of Web 2.0 has greatly affected the power and profitability of centralized internet platforms like Amazon and Google, allowing them to establish themselves as dominant forces in the online world. Meanwhile, Facebook’s user-focused approach helped make it the world’s most popular social network. Now, nearly two decades after Web 2.0’s debut, the emergence of Web 3.0 is generating widespread interest and discussion.
What is Web 3.0? When most people hear the term Web 3.0, numerous unstructured concepts such as games, virtual reality, blockchain, and the digital age may come to mind simultaneously. For some, it remains an unfamiliar concept. Web 3.0 is an intelligent, personalized internet based on the distributed technology of blockchain. In other words, it represents a new form of Internet environment that leverages the decentralized and trustless nature of blockchain to enable peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions among users in the Internet space, addressing various centralized issues derived from the conventional Web 2.0.
Gavin Wood, the co-founder of the Ethereum mainnet, where many decentralized finance (DeFi) projects are onboarded, envisions a positive future for the Web 3.0 market. He emphasizes that blockchain-based Web 3.0 can transcend the inherent consumption structure of Web 2.0, where the economic value of user-generated digital assets is not shared. With the new internet philosophy of decentralization and the connection of digital value, Wood foresees the possibilities of the Web 3.0 era.
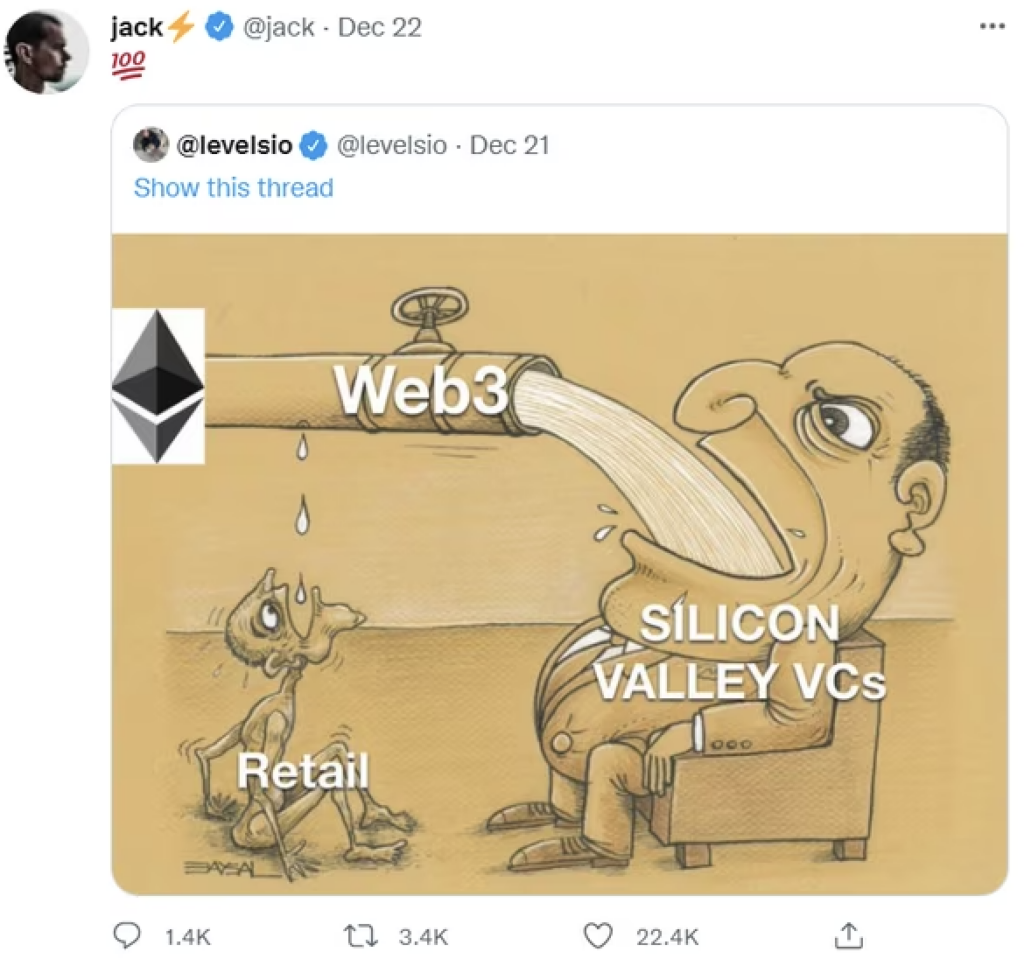
However, from the perspective of the mass adoption of the Web 3.0 industry, questioning the fundamental value of decentralization and whether there is sufficient trust among the public in using Web 3.0-based services, the author also acknowledges that there are still many unresolved issues. The present Web 3.0 discourse has faced criticism for resembling yet another centralized internet of empty illusions, with no significant difference from the existing centralized service structure of Web 2.0.
Let us recall that in 2021, the former Twitter co-founder Jack Dorsey directly criticized the utility of Web 3.0. During that period, numerous venture capitalists and investors in Silicon Valley showed interest in the new internet environment called Web 3.0 and the philosophy of decentralization, leading to a substantial influx of capital into the market. This influx of capital contributed to the allocation of significant funds for the growth of Web 3.0 and DAO, providing new opportunities for market expansion and fostering an expectation that it could accelerate the mass adoption of the Web 3.0 industry among the public.
However, Jack Dorsey and then-Tesla CEO Elon Musk expressed their thoughts on the intrinsic value of Web 3.0, stating on their Twitter accounts that the original discourse of Web 3.0 ultimately targets decentralization, but venture capitalists and their limited partners (LPs) ultimately aim to own it. The current direction of the Web 3.0 discourse leaves criticism, suggesting that it is just another centralized internet, no different from the past centralized service structure of Web 2.0.
In essence, for the mass adoption of Web 3.0, the growth of the blockchain-based industry relying on the centralized cloud services of Web 2.0 seems inevitable, challenging the past unique philosophy of Web 3.0. At the time, netizens asserted, “Web 3.0 is another vision for the future of the internet.” However, in terms of industry growth, it heralded the emergence of a new consensus in the discourse of Web 3.0, suggesting that it will not entirely replace Web 2.0 but move forward in a collaborative direction.
If the previous discourse of Web 3.0 was fundamentally about constructing a decentralized new ecosystem through disruptive innovation, now it signifies that, just as the consumption of smartphones has become universally prevalent in our lives without causing discomfort, the seamless integration into the daily lives of the masses is the primary sustainability of industry growth. One can easily find Web 3.0 services, such as centralized exchange (CEX) operating models and DeFi 2.0, resembling traditional finance, in our surroundings. Through this, it becomes evident that a newly agreed-upon discourse of Web 3.0 is beginning to take shape socially through the influence of both those supporting the unique philosophy of decentralization and those emphasizing the universalization of Web 3.0.
As for whether the choices made are the right direction for industrial growth, it is still difficult to make an accurate judgment. However, considering the influx of new capital and the universalization of Web 3.0 services accessible to the masses from the perspective of the mass adoption of the Web 3.0 industry, the trajectory of the newly agreed-upon discourse of Web 3.0 is expected to become a meaningful process in the development of the industry.

Looking ahead to 2024, we anticipate continued growth and development in the Web 3.0/crypto industry, which has become too big to ignore. This growth will be marked by the historic approval of Bitcoin ETFs by major asset management firms like BlackRock. Despite challenges related to lawsuits, arrests, and regulatory issues between the crypto industry and judicial authorities, 2023 can be evaluated as a year demonstrating robust recovery from adversities and downturns experienced in 2022.
This recovery is due to not only the approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs and technological infrastructure advancements for the scalability of the Ethereum ecosystem based on optimism and ZK-Rollup but also various crypto projects, ecosystem developments through airdrops on mainnets like Solana, and new technological advancements such as inscription – NFTs and FTs brought about by projects like Ordinals. These developments have instilled positive expectations among the public, leading many to believe that the Web 3.0 industry has the potential to become the “Next Big Thing.”

According to news reported by The Block in 2023, the approval of Bitcoin ETFs and the booming virtual asset market has coincided with an increase in the total supply of stablecoins. Data indicates that, following the peak in May of the previous year, which marked the end of the crypto winter that began in 2022, stablecoins showed a declining trend throughout the year. However, recent market enthusiasm driven by the surging Bitcoin rally has led to an increase in the total supply of stablecoins.
Glassnode analysts interpret the rise in the total supply of stablecoins as a positive signal within the crypto market, attributing it to increased demand from investors seeking exposure to speculative capital in the cryptocurrency industry. They analyze it as a positive sign that, along with the heightened interest from existing mainstream participants in the current Web 3.0 market, the substantial inflow of net capital into the overall crypto market indicates an upward trend. They diagnose, “The significant attention from investors towards the Bitcoin rally at the end of 2023, leading to the influx of fiat currency and user participation, is uplifting the entire crypto market, steering it towards a comprehensive upward trajectory.”
The former Binance’s CEO, CZ, discusses the imminent possibilities in the Web 3.0 market, stating, “While the existing Web 2.0 has formed vast ecosystems like Instagram, Amazon, and Google through simple technology for transmitting information, the convergence of new technologies and infrastructures formed on the blockchain, capable of transmitting value, could bring unimaginable potential (profit) to a new ‘ecosystem’.”
The new ecosystem of Web 3.0: The metaverse
Reflecting on the preceding parts, Web 2.0 is evaluated as an era of centralization dominated by centralized platforms and large corporations. In contrast, Web 3.0 aims to transcend the existing centralized consumption structure, emphasizing the preservation of the value of transparent and trustworthy user data. The unique philosophy of Web 3.0 in the past, coupled with the significant interest from businesses and further adoption within the legal framework of cryptocurrencies at the current moment, leading to the influx of new users’ capital, contributes to shaping a new social discourse within the Web 3.0 ecosystem. This, once again, indicates the emerging potential of the Web 3.0 ecosystem being reconfigured for the masses.
Many crypto companies emphasize that, unlike Web 2.0, the Web 3.0-centric industry goes beyond the role of transmitting information. It emphasizes the enormous potential profitability due to the ability to store new digital value through the innovative technology of blockchain. Therefore, within the newly structured discourse of Web 3.0, the resurgence of the metaverse is considered an attractive and innovative ‘ecosystem business model’ that can create a new revenue structure for user onboarding, similar to how Web 2.0’s e-commerce and platform-centric portal business models did, and is expected to play a significant role in shaping the current industrial ecosystem with considerable economic utility and potential.
Q: If so, what is a metaverse?
The term “metaverse” appeared in 1992 in Neal Stephenson’s novel. It is a portmanteau of “meta,” meaning transcendental, and “universe,” signifying space. In essence, the metaverse refers to a 3D virtual world where individuals use avatars or characters to escape from the real world and engage in daily activities and economic life within the digital realm. To today’s digital-native generation, the metaverse’s rapid rise is no longer a mere illusion; it is increasingly becoming a foundation for living and further development.
For them, this concept represents a new social perspective where they can carry out daily life and economic activities through virtual characters representing their personas. It implies they are willing to uphold real-life responsibilities and obligations, even extending equal social rights to their virtual characters, creating a new societal worldview that demands accountability.

Let’s take a Second Life, hailed as the pioneering archetype of past metaverse services, as an illustrative example. Second Life is currently recognized as the progenitor of all metaverse games, often acknowledged as the genesis of the metaverse gaming landscape. Founded by Philip Rosedale in 1999 through Linden Research, this virtual 3D environment allowed people to meet in virtual reality software, laying the foundation for contemporary metaverse projects.
The ecosystem structure of Second Life, akin to many current metaverse, involves the establishment of an autonomous economic system within its virtual world. Leveraging a virtual currency called Linden, users created and developed their metaverse spaces, engaging in real-life exchanges and transactions. The success of this project extended well into the late 2000s, transcending individual user experiences to include corporate entities. Users at the enterprise level utilized the platform not only for personal life extensions but also for pre-testing products, conducting internal meetings, and engaging in actual product transactions with the public.
Consequently, Second Life symbolized the success of a metaverse project to such an extent that it held significance and symbolism within the United States, a leading country in the field of IT technology at that time.

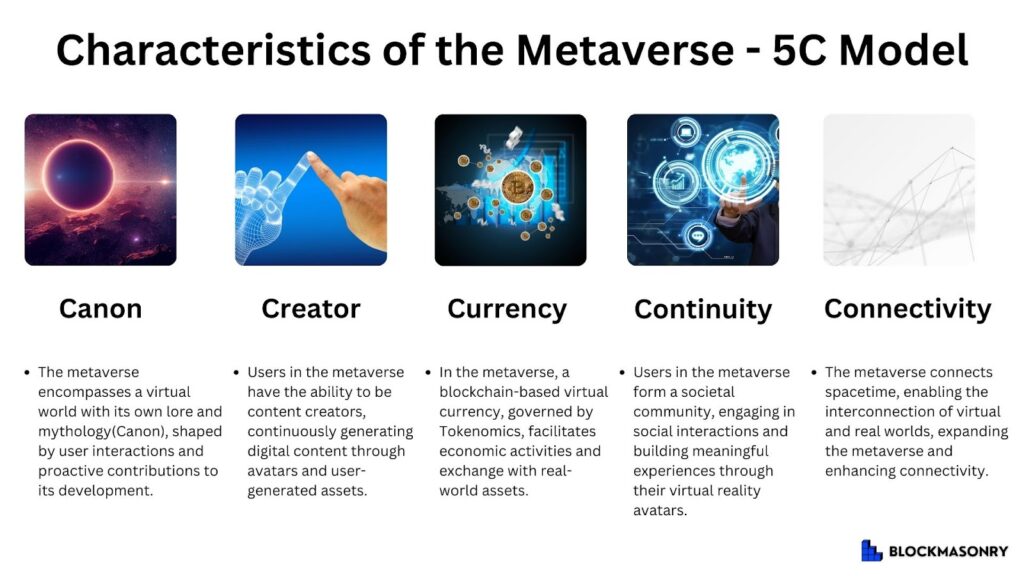
As evident from the described 5C Model of the metaverse, the metaverse is defined as a virtual space containing a new worldview or ideology, filled with active participation from users and creators, leading to the expansion of the worldview. This metaverse space serves as an extension of users’ everyday lives, and within its ecosystem, a new social community is formed through the use of Linden tokens, creating an economic system known as Tokenomics. By connecting socially with other entities within the virtual reality space, the metaverse establishes itself as a valuable space within Web 3.0, garnering attention as a profitable business model amid the current platforms.
Deloitte Consulting describes the rapid emergence of the metaverse as follows: “While the concept of the metaverse has been circulating for a long time, it has recently gained attention once again.” The advent of a new social worldview centered around the metaverse extends beyond individuals’ daily lives, permeating various industries. Deloitte identifies several factors contributing to the resurgence of the metaverse, notably social, technological, and industrial factors.
- Social Factors – The Rise of Remote Trends and Digital Natives
- Technological Factors – Technological Infrastructure Evolution for Implementing the Metaverse
- Industrial Factors – Opportunities for New Business and Industrial Ecosystems as the Next-Generation Platforms.
Comparing the software of Second Life with current metaverse services, it becomes evident that the contemporary metaverse, supported by advanced hardware and widespread software, holds a more substantial presence across people’s daily lives and industries. The surge of digital natives, catalyzed by the 2021 COVID-19 remote trend, advancements in previously lagging 3D technology and infrastructure, and sustained interest in the metaverse across various industries, all indicate the potential for significant profits in the Web 3.0 industry through the construction of metaverse ecosystems.
Therefore, Deloitte defines the current concept of the metaverse: “The metaverse is a next-generation profitable business model where real worlds converge, sharing virtual phenomena and experiences among various entities through interactions, generating new values through advanced economic, social, and cultural activities.” As a newly configured discourse in the Web 3.0 industry, the metaverse is leading us into a land of new opportunities. The paradigm of the metaverse is becoming an undeniable aspect of the next-generation Web 3.0 industry.
In March 2021, Roblox went public on the New York Stock Exchange, and in the same year, in October, Facebook rebranded itself as ‘Meta.’ This has led to a growing trend of high interest within the related industries that conceptualize the metaverse as an ecosystem alongside capital markets. Bloomberg Intelligence has predicted a future growth outlook for the metaverse industry of approximately $800 billion by 2024, while major players such as Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs estimate figures up to around $9 trillion. Big tech companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Google are also gearing up for a leap, preparing their own strongholds within the metaverse ecosystem. However, the era of deliberating over who will benefit from monopolistic advantages through the persistent centralized dominance of the Web 2.0 market seems to have come to an end.
On the other hand, the fundamental dilemma within the current industry revolves around how to adopt profitable business models and develop products to structure a massive ecosystem. Achieving widespread adoption of their services among the public and sustaining this popularity is predicted to be a fierce battle. As Deloitte defines the modern concept of the reconfigured metaverse, the preparation from a corporate standpoint is crucial in the evolving path of the metaverse’s development and the rapidly changing discourse of the new Web 3.0. Companies need to strategize for the next-generation popularisation of the industry within the metaverse’s evolving trajectory.
2.0 The Possibilities of Blockchain Gaming through the Reconceptualisation of Metaverse Games
The Convergence of Blockchain, Metaverse, and Gaming
Consequently, the future of Web 3.0 holds significant potential as a crucible, a Melting Pot, capable of amalgamating colossal technologies such as the metaverse and blockchain, ultimately converging towards the next-generation web paradigm. While individual technologies like blockchain and the metaverse are recognized for their substantial potential, it is believed that the convergence of emerging technologies in the Web 3.0 industry can create even greater synergies in terms of growth and universalization of services. The resurgence of the metaverse, as discussed earlier, is considered a significant opportunity that could bring about substantial changes across society. In other words, the metaverse in today’s Web 3.0 industry represents a crucial and potential milestone for companies to consider, not only as a lucrative new ecosystem business model but also as the Next Big Thing within the industry, poised for mainstream adoption and success.
Q: What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a data distribution technology that stores data in a decentralized manner. It connects blocks containing data into a single chain, following the concept of a ledger distributed across the network by participants. Unlike centralized structures of traditional data management, blockchain enables the collective recording and management of data on a peer-to-peer network without the need for specific institutions or central servers. The decentralized nature of blockchain within the Web 3.0 environment brings several advantages, connecting the significant value generated by users’ data. It provides high reliability and security, ensuring ownership rights over their assets. The emergence of blockchain technology extends its influence beyond the blockchain and Web 3.0 industries to impact various sectors. In response to this, the public poses one crucial question as follows.
Q: What can we do with tokenized coins? Can we apply them to games?
Traditionally, a game is defined as “a form of recreation in leisure activities where specific rules are established to introduce competition, enhancing the participants’ playful enjoyment, excluding labor in human life.” This definition can be broadened to encompass all play operated by silicon chip computer circuits possessing memory capabilities, particularly with the advent of the computer era. Hence, the term “computer games” has been used to replace the term for all play consumed within online spaces around us, reshaping its meaning.
Through the convergence of network-based computer technology, games have transcended their limited function of satisfying the desire for simple amusement in the traditional sense. Instead, they have evolved into a new form of gaming, combining cultural, industrial, social, and educational functions, all interconnected with the lives of the masses.
However, at the present moment, with the convergence of new technologies such as blockchain and the metaverse, the concept of games is once again undergoing a fresh reconstruction. Let’s briefly revisit the conceptual definition of the metaverse. Within the metaverse space, users must exhibit interoperability with the real world, spatial presence, simultaneity through socially formed communities online, and economic viability within the ecosystem utilizing blockchain-based tokens to be defined as a successful platform.
The current gaming market has consistently grown through the convergence of innovative technologies. In the 2000s, PCs and consoles took the lead, followed by a mobile-centric gaming market in the 2010s, leading to the diverse forms of the current gaming market.
Now, what does the current state of games utilizing blockchain look like? Successful AAA (Triple-A) game projects based on the established Web 2.0 have been dedicating considerable efforts to creating high-quality metaverse spaces within their game worlds, focusing on providing users with vivid experiences of simultaneity, interoperability, and spatial presence. This trend is noticeable, especially for those who have consumed large MMORPGs or MOBA-based game projects with verified game IPs on the Web 2.0 platform.
In contrast, blockchain games represent a new concept created by traditional game planners/metaverse creators emphasizing ownership and interoperability of in-game assets. In other words, blockchain games can be seen as games that advance interactive elements within the metaverse through innovative blockchain technology. This form of gaming can be defined as Play to Earn (P2E), where on-chain digital assets are distributed, and users participating in the game can directly utilize their tangible assets through a decentralized blockchain infrastructure for cryptocurrency in-game services.
Let’s explore the characteristics of Web 3.0-based Play-to-Earn (P2E) blockchain games:
- Enhanced Ownership and Transaction Transparency: Blockchain-based games improve the transparency of ownership and transaction history of user assets within the blockchain. By securely recording ownership and transaction details, users can gain high security and trustworthiness while playing the game. (Security and trustless)
- Utilization of Blockchain-based Digital Assets (Tokens): Users can utilize digital assets (tokens) based on the blockchain, including in-game items, characters, and tokens. (In-Economy)
- Activation of In-Game Economy: The use of tokens signifies the activation of the in-game economic system. Compared to traditional centralized Web 2.0 metaverse games, this enhances the scalability of assets within the ecosystem, promoting liquidity with other ecosystems.
- Empowerment of Incentive Systems: P2E games that provide individuals with control and ownership over assets strengthen the incentive systems within the game. (Incentive system)
These features are emphasized as crucial elements in shaping the in-game economic ecosystem within the gaming community and their created metaverse, playing a pivotal role in the formation of the current Play-to-Earn (P2E) blockchain games. Therefore, within the perspective of the current Web 3.0 paradigm, blockchain-based P2E games represent a novel concept wherein numerous enterprises leverage digital spaces imbued with their unique worldview on the new web environment. This signifies the birth of a gaming ecosystem business model that integrates new metaverse elements.

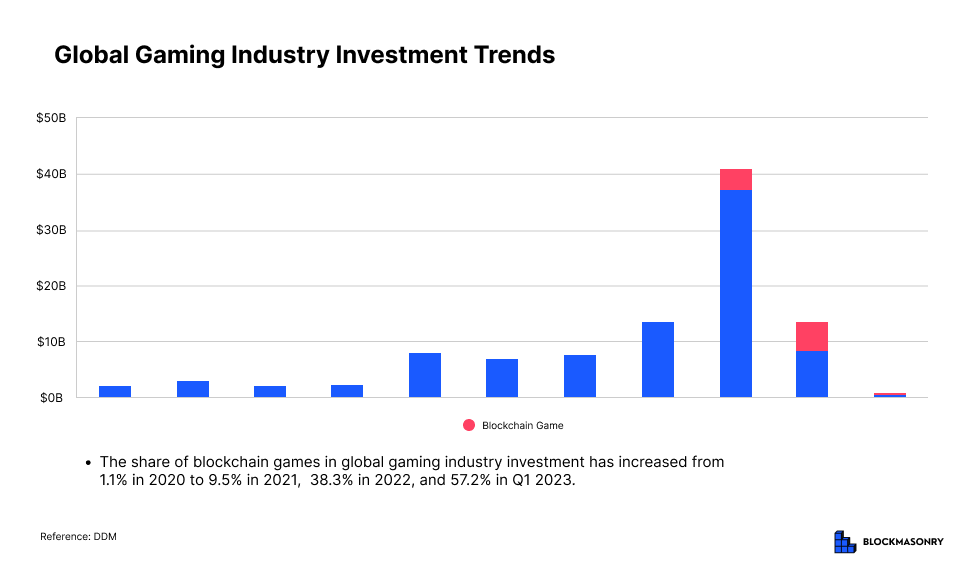
According to statistics from The Block and DDM, the blockchain gaming sector has been reported as the second-largest recipient of funding among areas closely related to the intersection of the metaverse and blockchain, following blockchain infrastructure development. In 2023, the cumulative investment in blockchain Play-to-Earn (P2E) based NFT games reached $16.3 billion, indicating that it received the second-highest capital infusion after blockchain infrastructure, which attracted a total investment of $20 billion. Considering that the gaming industry, excluding blockchain games, received capital inflows of $7.3 billion, $13.3 billion, and $8.3 billion in 2019, 2020, and 2022, respectively, it provides insight into the significant attention the blockchain gaming market is currently receiving within the overall market. Additional research data suggests that the proportion of blockchain games in total game industry investments has continuously increased from 1.1% in 2020 to 9.5% in 2021, 38.3% in 2022, and 57.2% in the first quarter of 2023.
These indicators reveal that the fundraising amount in the blockchain gaming sector is considerable, comparable to the traditional gaming industry. Simultaneously, the integration of blockchain technology and the new ecosystem business model called the metaverse provides a unique form of entertainment by offering users direct ownership and rewards for in-game assets, showcasing the immense potential of Play-to-Earn (P2E) blockchain games.
The question arises: Is the mass adoption of such blockchain gaming services genuinely achievable?
3.0 The Mass-Adoption of Blockchain Game
Creating a new gaming ecosystem on the blockchain implies liberating users who love traditional games from the role of mere game service consumers, elevating them to active participants who interact with the gaming ecosystem. This development is anticipated to set the stage for a new trend in the future gaming industry, despite the current difficulty in providing an immediate and clear answer regarding the extent to which blockchain games have become mainstream, given the influx of considerable attention and investment capital.
In light of this, we want to pose two questions.
- Is the Current Gaming Industry Adapting Effectively to the Rapidly Changing New Web 3.0 Paradigm?
- Can Blockchain-Based Games Truly Achieve “Next Big Thing” Status Amidst These Trends?
The Ultimate Manifestation of the Agile Gaming Trend: Blockchain Games
Q: Is the Current Gaming Industry Adapting Effectively to the Rapidly Changing New Web 3.0 Paradigm?
To respond to the first question, we will first look at the present state of the gaming sector. Many experts anticipated that the gaming industry would benefit significantly from the pandemic in 2021. According to the gaming industry research institution New Zoo, there was actual growth in the gaming market that exceeded expectations in 2020 and 2021. However, in 2022, external factors such as the global economic downturn and the endemic nature of the pandemic contrasted with these positive trends, providing users who played games with opportunities for actual environmental and structural changes. In other words, as the stringent pandemic measures eased, the outdoor activity time of users increased dramatically, leading to a simultaneous decrease in the usage time of mobile and PC games that were predominant at that time. The concentrated change in user game usage, driven by these external factors, led users to prefer new game genres introduced from the initial non-face-to-face environment of the pandemic. This, in turn, drew attention to blockchain-based games, which had yet to gain significant profitability in the market, as a new and profitable business model.
This phenomenon symbolizes another crucial turning point in the current Web 3.0 gaming industry trends. Present games have become more mainstream, and many gaming companies are experimenting with various business models, aligning with the new paradigm of Web 3.0, incorporating technologies such as the metaverse, AI, and blockchain to enhance their profitability. In other words, companies are emphasizing the importance of a new agile form of game ecosystem building, enriched with interactive elements of the metaverse that enable more realistic interactions among users alongside traditional IP franchise-centered marketing strategies.
Therefore, at this point, for companies to seize new market entry opportunities and adapt to current trends agilely, agile-focused ecosystem building is essential. Consequently, the current gaming industry is entering another significant adjustment period. This adjustment is expected to be more meaningful not only for traditional Web 2.0-based gaming companies but also for Web 3.0 companies based on blockchain.

The development of new technologies and the globally driven digitization centered around platforms have significantly altered the fundamental dynamics between traditional gaming companies and service users. Let’s consider an example. The heliocentric theory, which proposes that the Earth revolves around the Sun, took about 270 years to be widely accepted as the current consensus. Now, the heliocentric theory is considered a self-evident proposition, but at the time, the discourse surrounding the heliocentric theory, shaped by existing power relations, would have been a confusing concept for the general public.
A similar phenomenon is currently emerging in the gaming industry. In the past, games were dominated mainly by centralized, company-centric services. In game development, companies held the central influence over numerous objects that had the most impact on the service, and customers were relegated to the role of mere consumers orbiting around this centralized game service.
This logic is perceived as a similar problem to the unchecked development of various Web 3.0-based gaming companies that launched without considering the complexity of blockchain from the customers’ perspective. However, within the current trend, the development direction of gaming companies emphasizes encouraging user ecosystem participation/contribution, adapting to the interactive elements of the metaverse, and progressing through agile-centric ecosystem development based on blockchain.
The current attitude of companies striving to shape an agile-centric gaming ecosystem by integrating various new elements, such as DAO, tokenomics, blockchain, and the metaverse, aligns with the present trend in game development. This approach is considered an essential step that companies must take, not just for the short-term success or failure of their game projects, but as a crucial step towards shaping the Next Big Thing in the future game industry in the long run.
Q: Can Blockchain-Based Games Truly Achieve “Next Big Thing” Status Amidst These Trends?
However, existing Web 3.0 blockchain-based gaming companies with extremely short lifespans have primarily focused on maximizing immediate profits through the integration of blockchain and games in the form of Play-to-Earn (P2E) games. Nevertheless, the author believes that the development divergence of existing Web 3.0 gaming companies, which do not engage in customer-centric agile ecosystem game development, only serves further to exacerbate the Galapagosisation of the blockchain gaming market.
Unfortunately, the current state of blockchain gaming is not just a competition among Web 3.0 blockchain gaming companies but involves the adoption by existing Web 2.0 game users as well, leading to a form of gaming referred to as Web 2.5. The ultimate Next Big Thing will be realized when mainstream adoption and the complete influx of users into gaming services occur.
Therefore, one crucial aspect the gaming industry must consider going forward is the sustainability of the gaming ecosystem. In other words, it involves fundamental considerations about whether blockchain-based games can survive compared to traditional games. As briefly mentioned in the success factors of previous metaverse projects, the activation of Web 3.0 blockchain-based games fundamentally requires the construction of an ecosystem that is user-centric, encouraging active user participation. However, no matter how engaging a game may be, continuously attracting gamers, maintaining the sustainability of the game as participants in the ecosystem, and establishing regular updates and tokenomics (economic systems) for the game as a creator are challenging tasks.
Exploring Katz and Blumler’s Uses and Gratifications Theory in the Context of New Media and Blockchain-Based Games

In this context, Let’s briefly examine the Uses and Gratifications Theory proposed by Katz and Blumler in 1973. The theory elucidates a framework that clarifies the adoption relationship between services and users, particularly in light of the emergence of new media and services. Furthermore, it underscores the active role of individuals as selective agents regarding media, asserting that humans are fundamentally dynamic selectors rather than passive recipients. In essence, the theory emphasizes the active role of the audience in choosing and utilizing new media in a competitive landscape, highlighting the motivations influencing the adoption of specific media by active consumers. In other words, Katz and Blumler sought to elucidate through a theoretical approach what contemporary users (the audience) do through media such as games and identify the motivational factors influencing the selection and utilization of specific media.
The five premises of the Uses and Gratifications Approach are as follows:
- Media users are active and purposeful in their use of media.
- Users, in the process of utilizing media and seeking gratification, engage in media selection influenced by specific motivations.
- However, these media are always in competition with alternative means.
- Users are well aware of their interests and motivations.
- Furthermore, users, even when exposed to the same media messages, reconstruct values based on their individual motivations.
The theoretical framework of utilization and satisfaction for the new media discussed above provides crucial insights for Web 3.0 companies striving to foster an agile gaming ecosystem. It is academically meaningful, employing theory to analyze the noteworthy correlations to understand how blockchain-based gaming companies navigate their Web 3.0 businesses in competition with traditional Web 2.0 gaming companies in the current saturated gaming market and triggers for achieving mass adoption of blockchain games in the future.
According to a research paper conducted at Hanyang University in 2023, game users’ motivations were categorized into seven factors nationwide. The motivation factors include fantasy, entertainment and relaxation, social interaction, profit generation, curiosity, self-expression, and autonomy. The research results suggest that out of these seven motivations, only entertainment and relaxation, fantasy, and independence significantly impact satisfaction and the sustained intention of use.
Furthermore, according to a market research report on the U.S. gaming market released by the Entertainment Software Association (ESA) in June 2022, the age group with the most significant proportion of gamers is the 18-34 age group. Surveying this group, the report notes that “relaxation (57%)” and “fun (64%)” in ongoing gaming motivations significantly contribute to sustaining gaming usage. In other words, users actively engage in gaming for enjoyment, but equally significant is the use of games as a means of relaxation and recharge. This trend is expected to continue growing. Additionally, investigating users’ major assumptions regarding media adoption through theory becomes a significant analytical factor for ensuring sustainability in game development.
DappRadar conducted further research; however, only 16% of users downloading blockchain games continue to play them after the first day. This contrasts traditional games, where retention rates after the first day are typically around 50% as a critical counter thought.
Interestingly, games aspiring for mainstream adoption must ultimately provide users with entertainment and enjoyment. Analyzing motivational factors that can lead to user-centric adoption among competing games is a crucial aspect of enhancing the sustainability of game service production. Therefore, it is essential to address the challenges and limitations of blockchain games to ensure their long-term sustainability and success.
Sustainability of Blockchain Games: Significance of Entertainment and Hardware Accessibility
Historically, advancements in PC/mobile gaming technology and the proliferation of higher-spec hardware have significantly contributed to the progress of the modern gaming market. The gaming industry has undergone three major turning points – the console games of the 1980s, online PC games fueled by PC proliferation, and the contemporary era marked by the ubiquity of mobile devices. It can be observed that the current landscape of the gaming industry was preceded by the dissemination of hardware and technological evolution in each era until it gained acceptance among the masses.
The rapid internet speeds of Web 2.0 and the improvement in electronic device specifications led to graphic enhancements and frame rate improvements. This paved the way for the infrastructure of more immersive game modes such as high-spec MMORPGs, MOBAs, and FPS, providing users with a seamless gaming service environment that facilitated easier adoption of those gaming services.

However, what does the landscape of blockchain games look like today? Unlike traditional games, creating a game on the blockchain that can reproduce the high game quality of Web 2.0 is expected to be a challenging task.
Blockchain-based technology, particularly Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), which are digital assets that can prove ownership of the original (assets), is anticipated to synergize well with games where users play in the digital realm, collecting various items and engaging in gameplay. In response to these expectations, the first blockchain game utilizing NFT technology, CryptoKitties, was released in November 2017. Within just over a month of its launch, it recorded substantial revenue, selling NFTs of cats worth $25 each and generating an impressive $6.7 million.
Meeting the anticipation of the audience, 2018 saw the release of several popular blockchain games, including strategy tower web 2.0 games like Crazy Defense Heroes, trading card games like Splinterlands and Gods Unchained, and turn-based RPG games like Axie Infinity. Notably, Axie Infinity’s governance token, AXS, witnessed an extraordinary surge in market capitalization, soaring from $7.75 million on November 4, 2020, to a staggering $10.49 billion on November 8, 2021, marking an unprecedented 135,255% increase in just one year.
Q: So, when can we expect the mainstream adoption of blockchain games?
Despite the isolated successes of CryptoKitties and Axie Infinity, the current blockchain gaming industry has yet to achieve complete mainstream adoption. The reasons for this are akin to the decline of the metaverse project Second Life, as illustrated in the earlier section. While experts pointed to various reasons for Second Life’s decline, the predominant analysis attributed it to significant technological constraints at the time, such as the inability to simultaneously onboard a large number of users into the project ecosystem and implement all their game IPs. This was primarily due to technological limitations, including the constraints of content production and the low performance of early smartphones and network speeds, hindering the ability to stimulate user interest in gaming sufficiently.
This can be explained as the reason why current blockchain-based games have yet to undergo a complete revolution among the masses. The infrastructure and technological capabilities of past blockchain games could accommodate only simple play-to-earn (P2E) games based on casual genres, such as Axie Infinity and CryptoKitties. Such casual genre games demand relatively lower product specifications for playing compared to MMORPGs or high-spec quality games. However, this inevitably results in a lackluster gaming experience and content quality for users in the realm of casual genre games.
Due to the nature of blockchain networks, where all transaction information must be shared for security and stability, onboarding a highly complex high-spec game ecosystem onto a public Layer 1 blockchain involves technical limitations. The scalability issues of blockchain networks, due to their characteristic of sharing all transaction information, create difficulties in implementing highly complex high-spec game ecosystems on public Layer 1 blockchain.
As a gamer, experiencing lag during gameplay is frustrating. If, during an FPS game, my character suddenly dies due to a server error in the network, dissatisfaction with the service experience rather than the concept of entertainment may arise. If blockchain games are riddled with such glitches, the number of gamers willing to play such games may dwindle.
Ultimately, to sustain the new metaverse ecosystem based on blockchain and ensure its long-term popularity, game developers need to focus not only on simple casual games but also on enhancing the entertainment and fun aspects of games. In the era of active adoption of blockchain infrastructure for high-quality games, the long-term mainstreaming of the blockchain gaming industry may evolve. Therefore, game companies must emphasize moving beyond simple genres utilizing traditional NFTs and progressively developing their mainnet or proprietary game ecosystems. Adopting suitable business models from the current Web 3.0 paradigm and gradually developing their game infrastructure and high-quality content products is the direction to move towards.
As of 2022, there are a total of 3.2 billion gamers worldwide, with the Asian gaming market accounting for 52% of the total market, surpassing 1.7 billion users. As mentioned earlier, successful projects in the Asian market that achieved success with simple casual P2E-based games demonstrated the potential of blockchain games. Furthermore, large game companies from Web 2.0, such as WEMIX and Netmarble, holding strong IPs, are entering the Web 3.0 blockchain game market, strengthening the momentum of its growth.
Interestingly, there are plans for the release of notable AAA cryptocurrency games in 2023, with titles like Shrapnel, Guild of Guardians, and Illuvium generating anticipation among gaming enthusiasts. Notably, established NFT collection owners like the famous Yuga Labs, creators of Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC), attracted $450 million in investments in 2022. Unlike the past emphasis solely on profitability and new growth potential of simple NFT-based metaverse projects, they are making efforts within their own metaverse ecosystem called “OtherSide” to produce expanded high-quality metaverse content using a virtual currency called Apecoin. They aim to lead users’ entertainment through sustainable tokenomics. One positive aspect is that, along with the growth of the AR/VR hardware market, numerous game companies are entering the blockchain game market to create new revenue streams. Although current blockchain games must compete with traditional Web 2.0 games dominated by existing technology and hardware distribution, ongoing attempts by Web 3.0 game developers in terms of technical aspects of ecosystem building, such as Layer 2 solutions, Alternative Layer 1, sidechains and appchains, and rollups, demonstrate efforts to improve the scalability issues within their ecosystems while maintaining the exceptional security of blockchain for users.
Mass Adoption of Blockchain Games from a Medium to Long-Term Perspective
Educating existing users about the fundamental reasons why current game companies aim to launch their new business models based on non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and virtual assets called tokenomics using blockchain games, alongside technological advancements, will be crucial in shaping the Next Big Thing in the gaming industry. In other words, Web 2.0 users looking to engage in Web 3.0 games will not consume new forms of game content based on blockchain solely for the sake of solid asset security or transparent ownership of actual virtual assets. Similar to how Ethereum’s founder, Vitalik Buterin, felt the need for decentralization of his game items through the MMORPG genre of World of Warcraft before encountering blockchain, today’s blockchain games must emphasize the attractive benefits they offer to users, such as comparable game quality, entertainment, blockchain scalability, and infrastructure development, ensuring users’ rights at the protocol level through their tokenomics. This is a critical moment to reemphasize the appealing advantages that blockchain-based game projects can offer to users.
The current Web 3.0/virtual asset ecosystem is advancing rapidly in terms of technology. This poses a significant barrier for users to understand virtual asset markets, technical solutions for Web 3.0 game projects, and game usage methods. The user interface (UI) of blockchain-based services is significantly more complex and obscure compared to traditional game services. Moreover, just as any useful technology remains unused without significant time, cost, or appropriate education for its adoption, efforts by companies to onboard existing users in the future blockchain-based gaming market should continue.
From this perspective, the direction of current blockchain games focuses not on short-term mainstreaming but on long-term industrial growth. Therefore, the ultimate direction of the blockchain-based gaming market in the future envisions fierce competition among agile, collaboration-centered game projects that understand the current Web 3.0 paradigm well. They aim to build an intriguing game ecosystem with expanded economic viability through their unique entertainment and tokenomics, leveraging the unique characteristics of blockchain. It is anticipated that this will be intensely competitive as companies strive to create game ecosystems that are well-adopted by the masses.
4.0 Yooldo: The Next-generation Gaming Platform

Thus far, we have introduced the evolving discourse of Web 3.0 revolving around co-existence with Web 2.0 and infusion with the metaverse. This has set the backdrop for understanding Yooldo, an innovative blockchain gaming platform created in 2021. Yooldo is a multiverse of play-to-earn (P2E) games featuring titles such as TroublePunk: Cyber Galz and Random Pirate Defence.
The name “Yooldo” draws inspiration from the Korean folktale “ The Tale of Hong Gil-Dong”. This story revolves around a heroic outlaw leader who, much like Robin Hood, fights for justice by taking from the rich and corrupt to protect the poor. “Yuldo” represents a utopian world established by Hong Gil-dong, the story’s protagonist, in his quest for a just society where everyone has an equal opportunity for success. In this context, Yooldo empowers players by giving them greater control over their gaming experience and facilitating a more equitable and transparent economy.
Team Yooldo recently concluded a $1.5 million funding round, propelling its valuation to an impressive $13 million. This milestone underscores the confidence and trust investors have in Yooldo’s innovative approach to Web 3 gaming. The strategic support from investors includes double jumps. Tokyo, Manta Network, Neopin, Klaytn Foundation, and Presto Labs extend beyond financial backing; they encompass sharing invaluable insights and industry experience, which are instrumental in Yooldo’s growth and success. Noteworthy contributions from grant funding partners like Aptos Foundation, BNB Chain, Immutable X, and Oasys underscore the recognition of Yooldo’s creativity and potential in the Web3 gaming sphere. Furthermore, Yooldo’s participation in prestigious programs like the Consensys Scale Program and the Google for Startups Program reflects the legacy IT sector’s confidence in the team’s ability to develop a sustainable Web3 gaming platform. With these achievements and funds in hand, Yooldo is poised to enhance its offerings, improve technology, introduce more captivating games, and foster community expansion, ultimately making the platform even more engaging and rewarding for players.

What sets apart this pioneering venture is the repertoire of innovative features deployed in addressing the challenges of the GameFi industry. Their strategy involves (1) enhancing the Web 3.0 features, (2) embracing the Web 2.0 user experience, and (3) interconnectivity. Through these approaches, Yooldo is committed to becoming the gateway for Web 2.0 gamers to delve into the Web 3.0 world of decentralization and P2E mechanics.
The following section explores Yooldo’s features underpinned by the 3 strategies.
Enhancing the Web 3.0 features
Decentralized Governance and Anti-Cheat System (Jury DAO)

Despite Yooldo valuing the Web 2.0 gaming experience, the platform is by no means centralized. With decentralized governance unlocked with the $YOOL platform token, community-driven decision-making empowers users to shape the platform’s future, ensuring inclusivity and transparency. Yooldo’s governance model allows players to vote on new features and parameters of the platform and rewards them for their participation. The incentive pool includes a portion of in-game fees, marketplace fees, and NFT sales, providing additional benefits for players.
Team Yooldo has recently prepared a governance token airdrop program for existing and prospective community members. Through the airdrop program, users will be able to participate and be part of Yooldo’s ecosystem. Between 10% and a maximum of 20% of the total volume is allocated to the airdrops. The $YOOL token, earmarked for the ecosystem fund, will be immediately unlocked by 10% in the Token Generation Event and linearly vested over the next 20 months. Anticipating numerous forthcoming events, the team has allocated a flexible pool to encourage participation and distribute rewards to as many users as possible, constituting roughly 30% of tokens vested at the Token Generation Event.
Taking the concept of DAO to the next level, Yooldo introduces its novel fair game system, known as Jury Dao. League players can request a review of another player’s in-game conduct by putting up their participation fee as collateral. Other players review the match and decide if any cheating occurred. If malpractice is found, the accuser is rewarded, and the cheater is penalized. This system, with incentives enabled by blockchain technology, protects the integrity of the game against hackers.
Sustainable Multi-Token Economy
Sustainability concerning token value and user retention has been a long-standing challenge in the blockchain gaming industry. Learning from the experiences of its predecessors, Yooldo has implemented a multi-token system comprising the $YOOL platform token and various in-game utility tokens.
A platform tokenomics model connects a single platform token with in-game tokens of each game. Users acquire in-game tokens through gameplay, which can be exchanged for $YOOL before being sold on cash exchanges. For in-game purchases, users can buy $YOOL on exchanges and exchange them for in-game tokens within the platform. This model supports in-game economies and separates user and investor demand, preventing inflation of in-game tokens, high barriers to entry, and asset outflow.
Moreover, Yooldo aggregates the value of different games and IPs into $YOOL, granting $YOOL holders the voting ability on platform features, and they are rewarded for engagement. As in-game tokens are exchanged with the platform token based on a predetermined ratio, this ensures the stability of the in-game economy.
Moreover, Yooldo prides itself on its inflation-free tokenomics. The platform’s games facilitate the exchange of utility tokens at a fixed price, effectively preventing inflationary pressures. This stability is maintained by ensuring that none of the game’s utility tokens are subject to free minting. Instead, they operate on a reward distribution system driven by competition. However, to mitigate the risk of user attrition resulting from competition, Yooldo has implemented various mechanisms within the game.
In essence, Yooldo is committed to delivering a Web 2.0 gaming experience that liberates players from concerns about token value fluctuations. It ensures that players are fairly rewarded for their skills and support for the game while enjoying a seamless and enjoyable gaming experience.
Embracing the Web 2.0 User Experience
AAA Quality Games
In contrast to the financially oriented hypercasual games prevalent in the current GameFi landscape with relatively short life cycles, Yooldo is committed to delivering high-quality AAA games that have marked the Web 2.0 gaming era.
During an offline tournament event for Yooldo’s first title, Trouble Punk: Cyber Galz, held before the official launch, many users left positive remarks on the captivating game content and web 2.0 user-friendly experience it provided.

Furthermore, Yooldo’s games are designed to cater to a diverse player base, embracing both web2.0 and web3.0 gamers with varying skill levels. For instance, “Trouble Punk” incorporates an asset lending system that lowers the entry barrier for casual gamers. In addition, Yooldo’s latest mobile game, “Random Pirate Defense (RPD),” accommodates both Free-to-Play enthusiasts and Pay-to-Earn users, thus diversifying the player community.
Interconnectivity
Interconnectivity poses a significant challenge for both the metaverse and blockchain games.
On one hand, blockchain games have historically grappled with isolated gaming assets. Currently, many P2E games lack interoperability, and the blockchains hosting them are mostly independent. Transferring NFTs across gaming blockchains is often impractical, leading to siloed in-game assets.
On the other hand, in the classic model of the metaverse, items purchased in one world could only be used within that specific world. According to Sebastian Borget, the CEO of The Sandbox, most metaverse intellectual properties, including Roblox and Minecraft are considered microverses rather than true metaverses. Metaverses should have interoperability of assets between games, such as importing items from Roblox into Minecraft.
Yooldo, however, breaks free from this constraint by seamlessly interfacing with various blockchain networks, capitalizing on cross-chain interoperability. In Yooldo’s multiverse, players are empowered to utilize a single NFT across diverse games and applications within the Yooldo ecosystem.
This resonates with the notion of universalization, which is the mass adoption from the consumer’s perspective. Users no longer need to be concerned about the intricacies of various blockchain networks; what truly matters is the seamless experience and effortless navigation of the service. Yooldo’s commitment to fostering interoperability between chains and games in its ecosystem serves as a pivotal step for mass adoption.
Conclusion
In essence, Yooldo’s ultimate goal is simple yet profound: to provide an entertaining and enjoyable gaming experience that bridges the worlds of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, making gaming more accessible and engaging for all. The exploration of Yooldo and its multifaceted approach to blockchain-based gaming presents a compelling narrative of innovation and potential within the industry. Through the initial segment of this series, we have unpacked Yooldo’s commitment to reshaping the landscape of Web 3.0 by introducing sustainable tokenomics models, the DAO Jury system, and Play-to-Earn initiatives. As we navigate the evolving terrain of the metaverse and GameFi, Yooldo emerges as a beacon of progress, signaling significant strides toward the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology. By dissecting the features inherent in the Yooldo ecosystem, we have illuminated pathways for the broader blockchain gaming market to achieve long-term viability and societal integration. As we stand on the cusp of 2024, the momentum behind Yooldo underscores the transformative potential of blockchain in shaping the future of digital entertainment and beyond.
Crypto education is essential
For more information
Yooldo Homepage: https://www.yooldo.gg/
Blockmasonry Telegram Community: https://t.me/+D39y_W2wwj03MWQ0
Personal Note From MEXC Team
Check out our MEXC trading page and find out what we have to offer! There are also a ton of interesting articles to get you up to speed with the crypto world. Lastly, join our MEXC Creators project and share your opinion about everything crypto! Happy trading! Learn about interoperability now!
Join MEXC and Start Trading Today!



