Cryptocurrency is exciting. Everyone is trading left and right to make a profit. So, it is better to engage in spot trading or futures trading? Both methods offer unique advantages and come with their own sets of challenges. Let’s explore what each entails and see which one might be the best fit for you.

Understanding Spot Trading
Spot trading in the crypto market involves buying or selling cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or any other altcoin for immediate delivery. Essentially, you purchase the crypto at the current market price. Then, it gets delivered to your wallet almost instantly. Furthermore, the primary advantage of spot trading is its simplicity.
You buy cryptocurrency, hold onto it, and sell it later when the price appreciates. For example, you buy 1,000 MX tokens for $3.00 in January. Then, you sell all your MX tokens in March for $5.00. This gives you a clean profit of $2,000. This approach is straightforward and ideal for those looking to directly own digital assets.
What About Futures Trading?
On the other hand, perpetual futures trading is a popular derivative product in the cryptocurrency market. Unlike traditional futures contracts that have a set expiration date, they do not have an expiration date. This allows traders to hold their positions indefinitely, as long as they meet the margin requirements.
Key Features of Perpetual Futures
No Expiry Date
The most distinguishing feature of perpetual futures contracts is the absence of an expiration date. Traders can hold their positions as long as they like, provided they maintain sufficient margin to cover potential losses.
Funding Rate
To ensure that the price of perpetual futures contracts stays close to the spot market price, exchanges use a mechanism called the funding rate. The funding rate is a periodic payment exchanged between long and short positions. If the funding rate is positive, traders holding long positions pay traders holding short positions, and vice versa if the rate is negative. This mechanism helps anchor the contract price to the spot price.
Leverage
Perpetual futures trading allows for significant leverage, meaning traders can control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. Leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses, making it a powerful but risky tool. For example, with 10x leverage, a 1% move in the underlying asset’s price results in a 10% move in the trader’s position.
Margin Requirements
To trade perpetual futures, traders must post collateral, known as margin. There are two main types of margin: initial margin (the amount required to open a position) and maintenance margin (the minimum balance needed to keep the position open). If the account balance falls below the maintenance margin, the position may be liquidated to prevent further losses.
Example of Perpetual Futures Trading
Let’s say you want to trade Bitcoin perpetual futures on MEXC with 20x leverage. Here’s a simplified example:
- Opening a Position: You decide to open a long position when Bitcoin is trading at $10,000. You commit $500 as the initial margin.
- Leverage: With 20x leverage, your position size is $10,000 (20 times your initial margin).
- Funding Rate: Suppose the funding rate is 0.01% every 8 hours. If you hold the position for a day, you might pay 0.03% of your position size ($10,000), which is $3 in funding fees.
- Price Movement: If Bitcoin’s price rises to $10,500, the value of your position increases to $10,500, yielding a profit of $500. Since you used 20x leverage, this translates to a 100% return on your initial margin ($500 profit on a $500 margin).
- Margin Call and Liquidation: If Bitcoin’s price drops to $9,750, your position value decreases to $9,750, resulting in a $250 loss. If your losses exceed the maintenance margin, your position may be liquidated to prevent further losses.
Comparing Trading Fees
When it comes to trading cryptocurrencies, understanding the fee structure is crucial.
Trading Fees in Spot Trading
Spot trading generally involves fewer fees compared to futures trading. When you buy or sell cryptocurrencies on the spot market, you typically encounter a trading fee. It is often a percentage of the transaction value. Furthermore, the fees are separated into taker fees and maker fees.
For example, if an exchange charges a 0.2% fee and you buy $5,000 worth of Bitcoin, your maker’s fee would be:
Fee=$5,000×0.002=$10
Similarly, if an exchange charges a 0.2% fee and you sell $5,000 worth of Bitcoin, your taker’s fee would be:
Fee=$5,000×0.002=$10
In total, you will spend $20 USDT on your spot trading for this particular coin.
Trading Fees in Perpetual Futures Trading
In contrast, perpetual futures trading has a more intricate fee structure. Apart from the trading fee, there are fees for using leverage, known as funding rates, which can vary based on market conditions. Let’s consider an example:
Suppose you enter a Bitcoin perpetual futures contract with 20x leverage, committing $500 as the initial margin. Your position size would be $10,000 (20 times your initial margin). If the funding rate is 0.01% every 8 hours, and you hold the position for a day (three 8-hour periods), you would incur funding fees:
Daily Funding Fee=$10,000×0.0001×3=$3
Additionally, you will be required to pay maker and taker fees similar to how spot trading works.
Which is Better for You?
Both spot and futures trading come with their own risk profiles. Spot trading is generally seen as less risky because you fully own the cryptocurrency and there’s no leverage involved. However, this also means your potential returns are directly tied to your initial investment.
Futures trading, with its leverage, offers the possibility of higher returns on smaller capital. However, it comes with a corresponding increase in risk. A wrong move in futures trading can not only wipe out your initial margin but also result in additional losses due to the leveraged nature of trade. Furthermore, futures trading fees tend to be more costly. This is because you can open and close a lot of trades with a small capital. The fees will then slowly eat away a margin of your profits.
How To Reduce Trading Fees
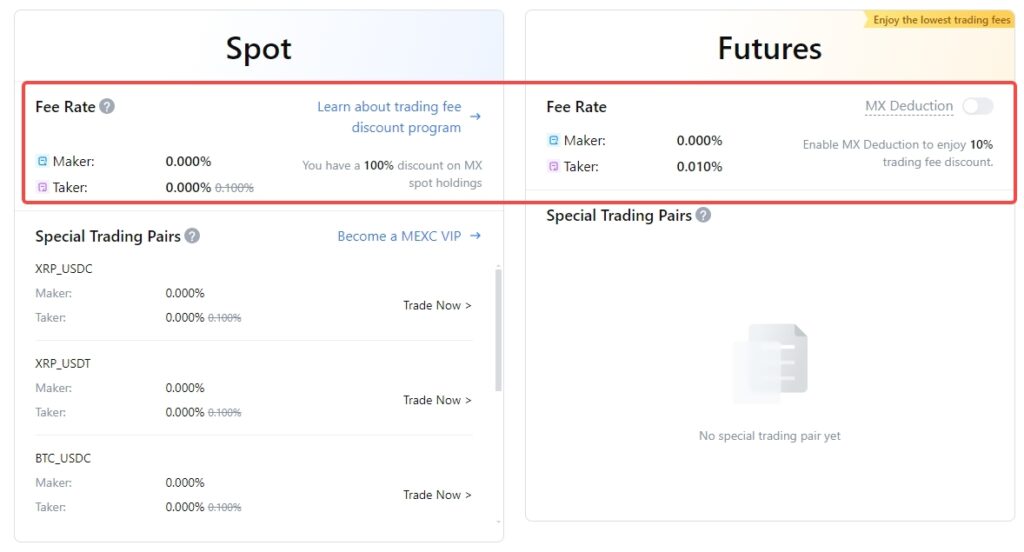
Trading fees might seem insignificant. However, it will bolster into a huge amount in the long run. Therefore, MEXC is the best crypto exchange for minimizing costs. MEXC offers the lowest fees in the entire crypto market, providing significant savings for traders. At MEXC, users can enjoy 0.000% maker and only 0.100% taker fees on spot trading. Meanwhile, futures trading is equally attractive with a 0% maker fee and just a 0.010% taker fee.
Additionally, by holding as few as 1,000 MX tokens for 15 consecutive days, users can enjoy up to 100% trading fee discounts for spot trading, effectively reducing costs to zero. For futures trading, users can benefit from a 10% discount via MX token deduction, further cutting down on trading fees. These features make MEXC an excellent choice for traders looking to maximize their profits by minimizing the impact of fees on their trades. Join MEXC now and enjoy the lowest fee in the market!
MEXC Will Add Excitement Into Your Trading Journey
Do you know that MX tokens are more rewarding than any other tokens on MEXC? Benefits, discounts, free airdrops, and even referral fees are all yours to receive!
Explore the benefits of holding MX Tokens right here: Why Should You Hold MX Tokens
Furthermore, MEXC provides up to 70+ free airdrops every week! Participation is easy and the reward is huge.
Learn all about the industry leader in airdrops: MEXC – The Best Airdrop Platform in The Crypto Market
Join MEXC and Get up to $10,000 Bonus!
Sign Up


