Futures trading represents one of the most sophisticated yet misunderstood segments of cryptocurrency markets. While MEXC’s futures offers leverage up to 500x and comprehensive risk management tools, statistical analysis reveals that approximately 90% of new futures traders experience significant losses within their first month of trading. This outcome occurs not due to platform limitations or market manipulation, but rather from fundamental misunderstandings about leverage mechanics, risk management principles, and psychological factors that govern leveraged trading success.
This comprehensive analysis examines the structural elements of successful futures trading on MEXC, addressing common failure patterns while providing actionable frameworks for sustainable leveraged trading strategies.
Understanding Leverage Mechanics and Risk Amplification
The primary misconception surrounding futures trading involves treating leverage as a profit multiplier rather than understanding its fundamental nature as a risk amplification tool. When MEXC offers leverage ratios up to 500x, this creates position control capabilities that far exceed available capital, fundamentally altering both profit potential and loss exposure in ways that most traders underestimate.
Mathematical Risk Analysis
At 500x leverage, traders require only 0.2% margin to maintain positions, meaning adverse price movements of just 0.2% result in complete position liquidation. Given that Bitcoin (currently ~ $112,000) typically experiences daily volatility ranges of 2–5%, and Ethereum (currently ~ $4,200) often exceeds 3–6% daily ranges, the mathematical probability of liquidation becomes virtually certain under such extreme leverage conditions.
Case Study: Leverage Impact on Position Survival
Consider a trader opening a long Bitcoin position at $112,000 using 500x leverage. The required margin represents 0.2% of position value, establishing a liquidation price at approximately $111,776 just 0.2% below entry. During a typical trading session, Bitcoin regularly experiences intraday fluctuations far exceeding this threshold, resulting in near-immediate liquidation despite potentially favorable longer-term price direction.
Historical analysis of Bitcoin’s price action reveals that 500x leveraged positions experience liquidation orders of magnitude more frequently than even 50x positions, with virtually no tolerance for adverse intraday noise. This statistical reality underscores the critical importance of leverage selection in determining trading outcomes. At 500x, survival becomes almost entirely dependent on luck and execution speed rather than market analysis.
MEXC Platform Architecture and Risk Management Integration
MEXC’s futures trading interface incorporates sophisticated risk management tools designed to address common trader behavioral patterns and mathematical risk exposure. Understanding these mechanisms proves essential for effective platform utilization.
Margin System Analysis
MEXC employs both isolated and cross-margin systems, each serving distinct risk management purposes:
- Isolated Margin Mode: Segregates margin requirements for individual positions, preventing single trade failures from affecting overall account equity. This approach proves optimal for beginners and provides granular risk control for experienced traders managing multiple positions.
- Cross Margin Mode: Utilizes entire account balance as collateral for all positions, offering greater flexibility but introducing systemic risk exposure across all active trades.
Figure 1: MEXC Order Interface – Risk Parameter Display
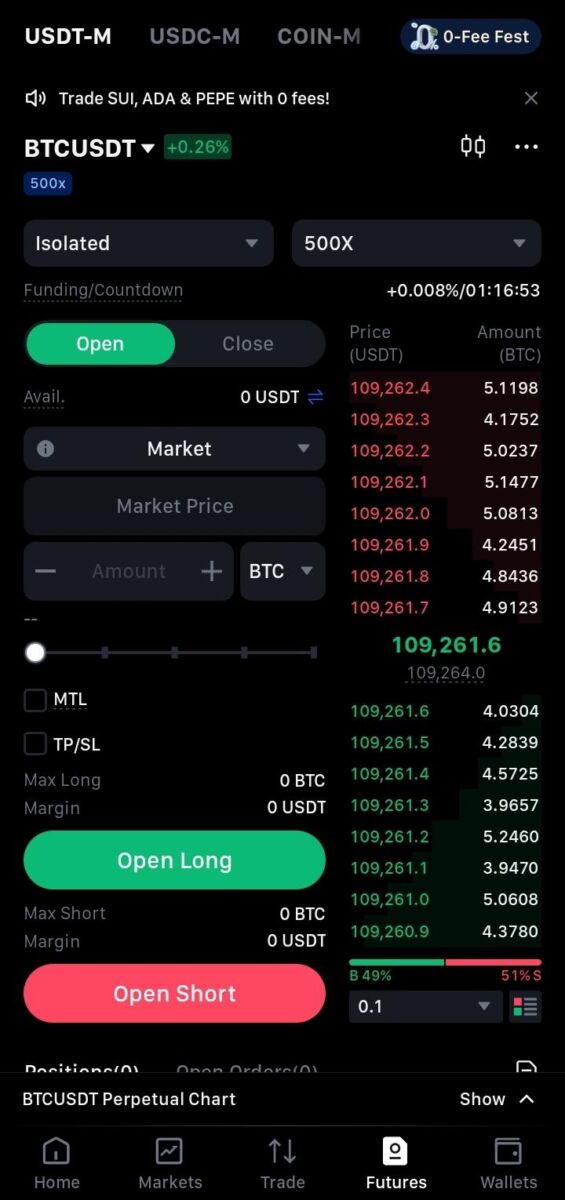
Position Sizing and Risk Calculation Framework
Professional traders employ systematic position sizing methodologies that determine appropriate leverage based on predetermined risk parameters rather than arbitrary leverage selection. MEXC’s interface supports this approach through integrated calculation tools.
Risk-Based Position Sizing Formula:
Position Size = (Account Risk Percentage) ÷ (Stop-Loss Distance Percentage)
Practical Application Example:
- Account Balance: $10,000
- Maximum Risk Per Trade: 1% ($100)
- Technical Stop-Loss: 2% from entry
- Calculated Position Size: $100 ÷ 2% = $5,000
- Required Leverage: $5,000 ÷ $100 = 50x
This methodology ensures that leverage selection stems from risk management requirements rather than profit maximization desires, significantly improving long-term sustainability.
Advanced Order Types and Execution Strategies
MEXC provides sophisticated order types that enable professional-level trade management when properly implemented. Understanding these tools’ strategic applications can substantially improve trading outcomes.
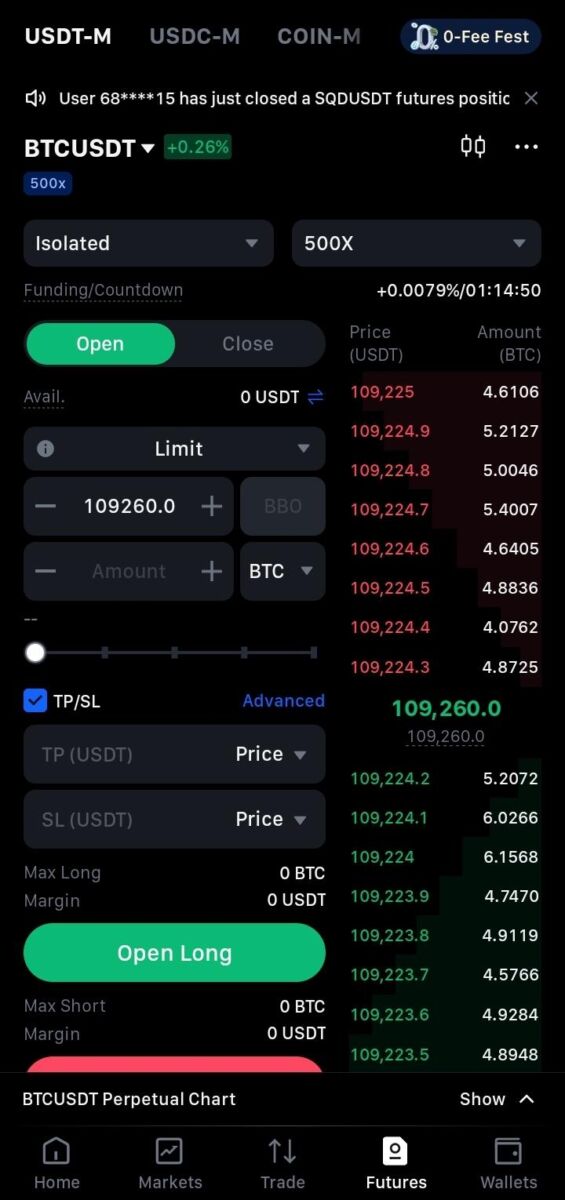
Bracket Order System Implementation
MEXC’s bracket order functionality allows simultaneous configuration of entry, stop-loss, and take-profit orders, eliminating emotional decision-making during position management. This systematic approach proves particularly valuable during high-volatility periods when rapid price movements can trigger psychological responses that override rational risk management.
Figure 2: MEXC Bracket Order Configuration
Conditional Order Applications
Professional traders utilize MEXC’s conditional order types to implement sophisticated entry and exit strategies:
Stop Orders: Trigger market orders when predetermined price levels breach, enabling trend-following strategies and breakout trading approaches.
Stop-Limit Orders: Combine price triggers with limit order execution, providing price control during volatile market conditions.
QTrailing Stop Orders: Automatically adjust stop-loss levels as positions move favorably, capturing trend momentum while maintaining downside protection.
Psychological Factors and Behavioral Risk Management
The integration of leverage with real-time position monitoring creates psychological pressures that significantly influence trading decisions. Understanding and mitigating these factors proves essential for sustained success.
Cognitive Bias Impact on Leveraged Trading
- Loss Aversion: Amplified by leverage, this bias leads traders to maintain losing positions longer than rational analysis would suggest, often resulting in liquidation rather than controlled losses.
- Overconfidence Effect: Early profits from successful leveraged trades frequently generate excessive confidence, leading to position size increases and leverage escalation that eventually produce significant losses.
- Recency Bias: Recent trading outcomes disproportionately influence future decision-making, causing traders to abandon systematic approaches after short-term results.
Systematic Approaches to Psychological Risk Mitigation
Professional traders implement mechanical trading rules that remove emotional decision-making from critical trade management functions:
- Pre-Trade Planning: Complete risk assessment and exit strategy determination before position entry eliminates in-trade emotional interference.
- Automated Risk Management: Utilizing MEXC’s automated stop-loss and take-profit functionality ensures predetermined risk parameters remain enforced regardless of emotional state during trade execution.
- Position Size Consistency: Maintaining consistent position sizing based on mathematical risk calculation rather than conviction levels prevents emotional position scaling that often leads to disproportionate losses.
Market Structure Considerations and Timing Optimization
Successful futures trading requires understanding broader market structural factors that influence leveraged position outcomes beyond individual trade analysis.
Funding Rate Analysis and Strategic Implications
MEXC’s perpetual futures contracts utilize funding rates to maintain price convergence with underlying spot markets. These periodic payments between long and short positions create strategic considerations for position timing and holding periods.
- Positive Funding Rates: Indicate long position dominance, requiring long holders to pay short holders. Sustained high positive funding rates often precede market corrections as overleveraged long positions face liquidation pressure.
- Negative Funding Rates: Suggest short position excess, with short holders compensating long holders. Extreme negative funding rates frequently occur near market bottoms, offering contrarian long opportunities.
Volatility-Based Strategy Adaptation
Market volatility conditions require strategic approach modifications to maintain effectiveness:
- High Volatility Periods: Require reduced leverage utilization and wider stop-loss placement to accommodate increased price fluctuation ranges while maintaining position integrity.
- Low Volatility Conditions: Enable higher leverage utilization but demand careful attention to breakout potential and range-bound trading strategies.
- Volatility Transition Phases: Often provide optimal futures trading opportunities as markets shift between consolidation and trending phases, but require rapid strategy adaptation.
Advanced Risk Management Techniques
Beyond basic stop-loss implementation, professional futures trading involves sophisticated risk management approaches that address various market scenarios and portfolio considerations.
Hedging Strategies Using MEXC Futures
Experienced traders utilize MEXC’s futures platform for portfolio hedging rather than purely speculative purposes:
- Spot Position Hedging: Opening short futures positions to offset long spot holdings during anticipated market corrections while maintaining long-term investment positions.
- Cross-Platform Arbitrage: Leveraging price discrepancies between MEXC futures and other platforms’ spot or derivatives markets for risk-controlled profit generation.
- Volatility Trading: Utilizing futures positions to capitalize on volatility expansion or contraction while maintaining market-neutral directional exposure.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Futures Trading Capabilities
Professional futures trading on MEXC requires integration of technical platform knowledge, sophisticated risk management techniques, and psychological discipline. Success stems not from prediction accuracy but from systematic risk management implementation and consistent execution of proven methodologies.
MEXC provides comprehensive tools for professional-level trading, but effectiveness depends entirely on trader education, disciplined implementation, and realistic expectations regarding both profit potential and risk exposure. Most importantly, futures trading should complement rather than replace foundational spot trading knowledge and broader cryptocurrency market understanding.
Traders who achieve consistent profitability in futures markets typically demonstrate several key characteristics: systematic approach to risk management, emotional discipline during adverse market conditions, continuous strategy evaluation and improvement, and realistic assessment of their own capabilities and limitations.
For those committed to developing professional futures trading capabilities, MEXC’s offers the necessary infrastructure. However, success requires significant education, practice with minimal position sizes, and gradual scaling based on demonstrated competence rather than optimistic projections about trading abilities.
The difference between successful and unsuccessful futures traders rarely involves superior market analysis capabilities. Instead, it reflects differences in risk management discipline, psychological preparation for leveraged trading pressures, and systematic approach implementation regardless of short-term trading outcomes.
Disclaimer: This content is for educational and reference purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Digital asset investments carry high risk. Please evaluate carefully and assume full responsibility for your own decisions.
Join MEXC and Get up to $10,000 Bonus!
Sign Up
