
In Q2 2025, Ethereum saw impressive growth fueled by Spot ETF inflows and greater institutional adoption. Surprisingly though, the Layer-2 (L2) ecosystem—long considered Ethereum’s growth engine—remained almost “flat.” This raises a key question: are Ethereum L2s hitting a wall right now?
1.On-Chain Metrics
1.1 TVS – Total Value Secured
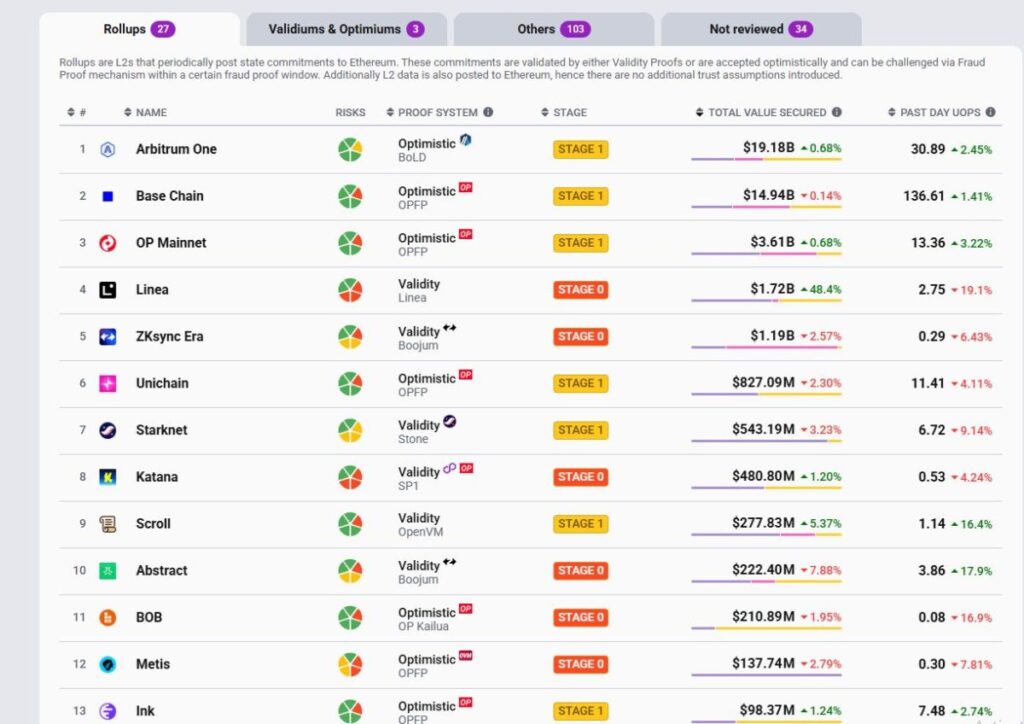
Unlike TVL, TVS gives a more accurate picture of Layer2 strength.
- Arbitrum currently leads with $19B TVS, driven by RWA inflows.
- Base is the most active L2 but ranks second with $14B TVS.
- Optimism and Linea follow, but the top 4 have already pulled far ahead of the rest.
The L2 TVS landscape today is highly concentrated around Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism, with Arbitrum clearly in the lead and Base consolidating a strong #2 position.
1.2 Transactions
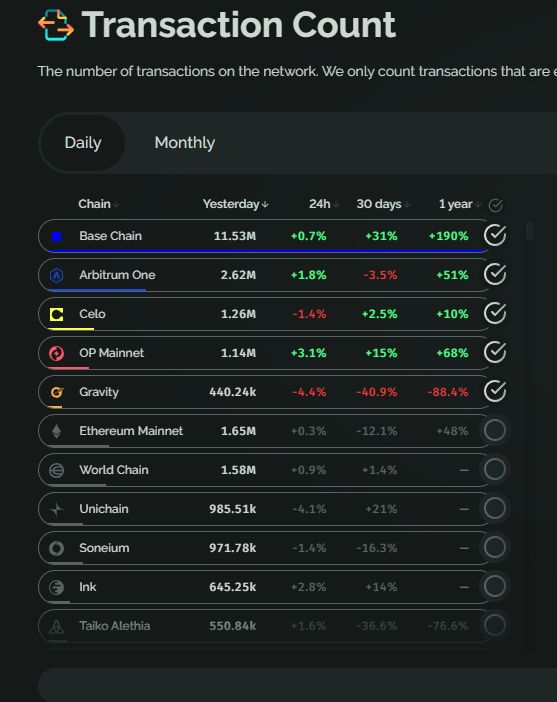
Daily transactions show Base in absolute dominance with ~11M tx/day, far ahead of any competitor.
- Arbitrum ($ARB) and Celo($CELO) form the second group but still lag significantly.
- Other L2s like Gravity, Linea, Mantle are losing momentum and sliding down the rankings.
The transaction market is consolidating around Base and Arbitrum, with Base pulling ahead thanks to Coinbase-driven ecosystem growth, large trading volumes, and effective incentive campaigns.
1.3 Revenue
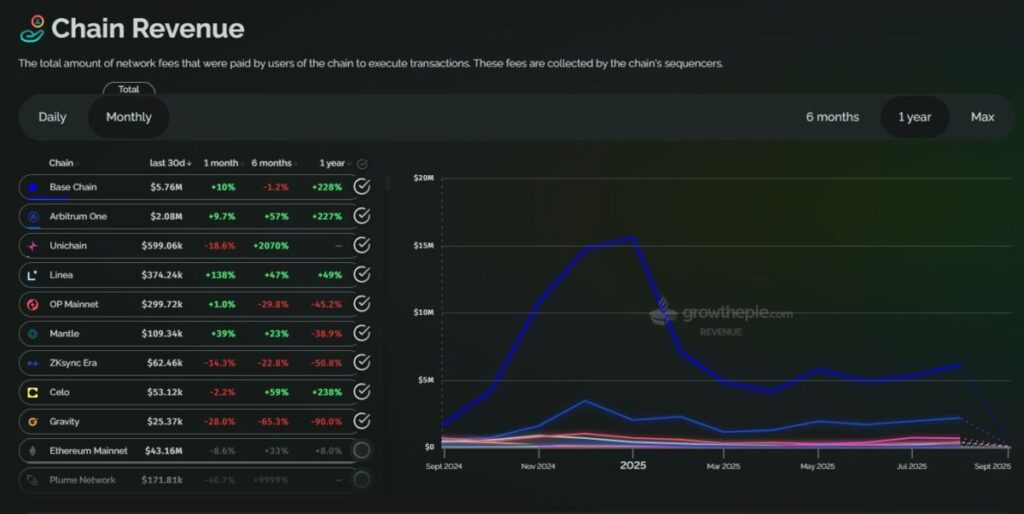
The revenue picture tells the same story.
- Base is dominating, reflecting its strong and sustainable growth.
- Arbitrum is #2, generating around $2M/month, but still far behind Base.
- Most others—Blast, zkSync Era, Mantle, Linea—can’t even break $500K/month.
This shows that while some chains can boost DAUs via incentives or airdrop farming, converting that into real revenue via sequencer fees is still a struggle.
OP Rollups (Base, Arbitrum) are decisively outperforming zk Rollups (zkSync, Starknet) across all major metrics: revenue, active wallets, transactions, and economic efficiency.
Right now, the L2 race is essentially Base vs. Arbitrum.
1.4 Price Performance vs. Other Sectors
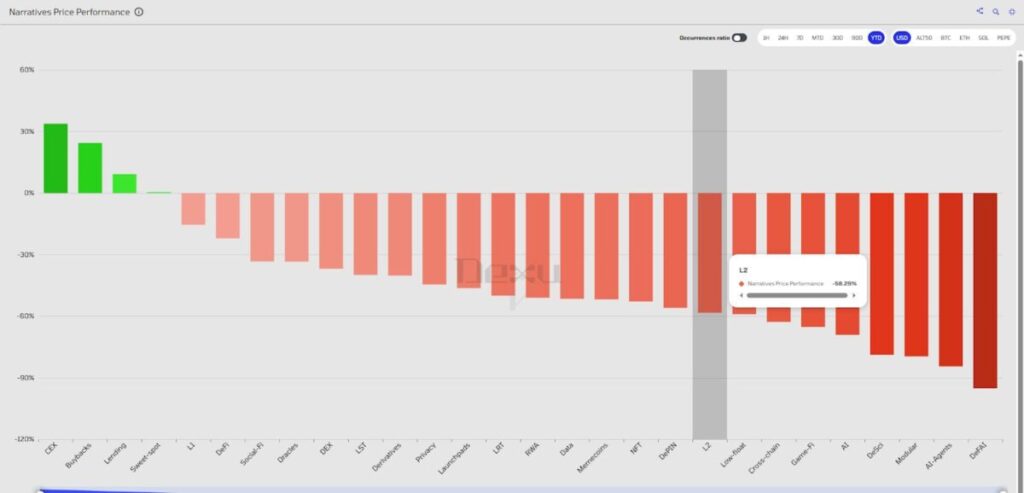
Despite solid on-chain growth, L2 tokens have been among the worst-performing sectors in terms of price. Revenue and fees are there, but no real buy demand has formed—something we’ll break down later.
2. Notable Technical Updates
2.1 Faster Block Times (<250ms)
As L2s don’t need to optimize for decentralization from day one, they’ve been prioritizing faster throughput and lower gas costs. Recent upgrades include:
- Base: Flashblocks (200ms miniblocks on top of 2s blocktime). Using Flashbots’ tech, Base is now the fastest EVM chain with near-instant confirmation.
- Arbitrum: Timeboost with default 250ms blocktime (down to 100ms). This optimizes MEV, reduces congestion, and enables faster priority transactions.
- MegaETH (testnet): 10ms blocktime, 20k TPS, aiming for 100k TPS with sub-ms latency via centralized sequencer + high-end hardware. Branded as “real-time Ethereum” for ultra-high-speed apps.
2.2 Solving Interoperability & Fragmentation
Scaling via L2s inevitably fragments liquidity and users. Current solutions include:
- OP Superchain: A family of L2s built on OP Stack, aiming for seamless connectivity, shared security, and unified liquidity.
- Adoption: Base, Optimism, World Chain, UniChain, Celo.
- zkSync Elastic Chain: Ecosystem of ZK-based chains (rollups, validiums, volitions) secured via zk-proofs.
- Adoption: Abstract chain (Pudgy Penguins), pushing native account abstraction + NFT trading.
- Arbitrum Orbit: Framework for customizable L2/L3 deployment on Arbitrum Nitro with native interoperability.
- Adoption: XAI, Robinhood.
So far, interoperability remains a priority, but no fully working solution has emerged.
3.Key Challenges
3.1 Centralized Sequencers – L2’s Biggest Weakness
Most major L2s (Base, zkSync, Linea, Scroll, Optimism, Arbitrum) rely on a single sequencer, which boosts efficiency but creates systemic risk.
- Example: In July 2025, Base (Coinbase’s L2) went down for 30+ minutes when both its main and backup sequencers failed. Users couldn’t transact, withdraw, or even access data.
This raises doubts: can L2s really claim to inherit Ethereum’s “never down” philosophy?
Worse, when sequencers fail, UIs and RPC endpoints stop responding, making withdrawals practically impossible—even if data availability exists in theory. Sequencers can even censor withdrawal requests.
One proposed fix: based rollups—integrating sequencers directly into Ethereum L1 validator sets. But this model is still early and not yet deployable at scale.
3.2 L2 Tokens – Weak Growth Drivers
Native L2 tokens mostly lack meaningful utility:
- Not used for gas.
- Not staked for network security.
- No share of sequencer revenue.
Examples:
- Base generated ~$93M in sequencer revenue over 12 months—without needing a token.
- Arbitrum earns ~$20M in fees, but ARB doesn’t capture that.
- Optimism also doesn’t share revenue despite Superchain expansion.
→ This leaves no natural buy pressure, while investor unlocks add constant sell pressure. As a result, L2 tokens have been one of the worst-performing categories in the past 2 years.
3.3 Liquidity Fragmentation & Poor UX
While L2s bring lower fees, they also fragment liquidity and complicate UX:
- Optimistic rollups: ~7-day withdrawal.
- ZK rollups: ~1-day withdrawal.
- By mid-2025, there are 20+ L2s—each with its own RPC, explorer, and UI. Cross-L2 transfers require bridges (slow, costly, risky).
For newcomers, every L2 feels like “starting from scratch.” This steepens learning curves and drives users away.
Meanwhile, L1s like Solana or NEAR/TON with sharding deliver smooth UX: unified wallets, fast transactions, low fees. This helps explain Solana’s strong TVL and DAU comeback in 2024–2025, despite L2’s technical advances.
4.What Value Do L2s Bring to $ETH?
Ethereum L1 secures L2s, but the economic value flowing back to ETH is minimal, creating misalignment.
- After EIP-4844 (Dencun, 2024), rollup data posting costs fell 88–99%.
- Previously, rollups paid hundreds of ETH/day in calldata, contributing significantly to ETH burn via EIP-1559.
- Post-Dencun: many L2s now spend only tens of USD per batch, cutting ETH burn from ~15,000 ETH/150 days pre-Dencun to just 3–4 ETH/day.
Impact: L2 activity surged, but value capture for ETH collapsed—weakening the “ultrasound money” thesis and leaving ETH underperforming.
Potential fixes:
- Based rollups: Ethereum validators as sequencers, routing revenue back to ETH.
- Shared sequencing markets: distributing fees to ETH stakers/restakers.
5.Conclusion
Ethereum L2s remain central to Ethereum’s scaling roadmap: cheaper fees, higher throughput, and alignment with major L1 upgrades like EIP-4844 and the upcoming Fusaka update. They’re becoming a crucial application layer, enabling everything from DeFi to RWAs.
But challenges persist: centralized sequencers, fragmented liquidity, weak tokenomics, and poor economic alignment with L1. While on-chain activity is booming, L2 tokens underperform badly, leaving this sector struggling to meet the hype.
Disclaimer: This content does not provide investment, tax, legal, financial, or accounting advice. MEXC shares information purely for educational purposes. Always DYOR, understand the risks, and invest responsibly.
MEXC'ye Katılın ve Bugün Ticarete Başlayın!



